Heap은 우리가 우선순위 큐를 구현할 떄 빈번히 사용됩니다. 우선순위 큐란, 우선순위가 높은 것 먼저 빠져 나가는 것을 말합니다.
Max Heap
max(min) tree란 parent의 key가 child의 키보다 작지 않은 것을 말합니다. 그리고 max(min) heap는 complete binary tree로써, max (min) tree인 것을 말합니다.
즉 max (min) tree에서 root의 값은 최댓값이거나 최솟값이 될 수 밖에 없습니다.

또한 이들은 complete binary tree이기 때문에 우리는 array representation으로도 heap을 나타낼 수 있습니다.
Insertion into a Max Heap
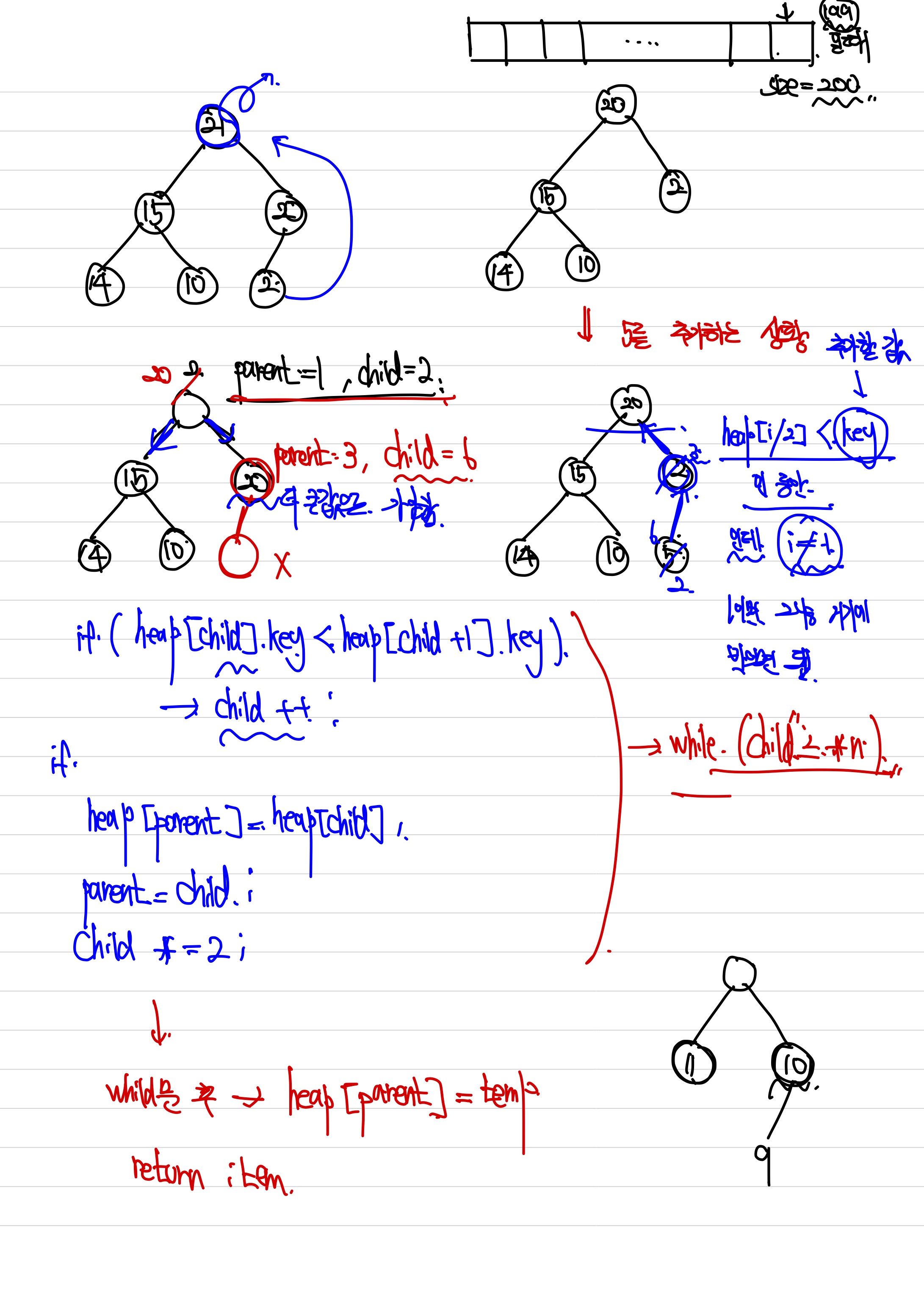
여기서 저희는 bubble up process라는 것을 정의해야 합니다. 이는 새로운 node의 시작점으로부터 위로 올라가면서 이 새로 추가될 노드의 새로운 자리를 찾아가는 과정입니다.

그 다음으로는 trickle down입니다. 이는 맨 위 즉 root값을 빼고 가장 마지막의 값을 위로 올려가면서 아래로 비교하며, 그 값이 삽입될 값을 찾아가는 과정입니다.

간단히 bubble up process와 trickle down process를 알아 보았으니, c언어 코드로 작성해 보도록 하겠습니다.
/heap.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define MAX_ELEMENTS 200 #define MAX_ARR_SIZE 1000 #define HEAP_FULL(n) (n == MAX_ELEMENTS - 1) #define HEAP_EMPTY(n) (!n) typedef struct { int key; } element; element heap[MAX_ELEMENTS]; int n = 0; void iterInorder(element heap[], int size) { int stack[MAX_ELEMENTS]; int top = -1; int i = 1; while (1) { while (size >= i) { top++; stack[top] = i; i = i * 2; } if (top == -1) return; i = stack[top]; top--; printf("%d ", heap[i].key); i = i * 2 + 1; } } void push(element item, int *n) { int i; // 만약에 HEAP이 꽉 찼다면 에러 if (HEAP_FULL(*n)) { fprintf(stderr, "The heap is full. \n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } i = ++(*n); while ((i != 1) && (item.key > heap[i / 2].key)) { heap[i] = heap[i / 2]; i /= 2; } heap[i] = item; } element pop(int *n) { int parent, child; element item, temp; if (HEAP_EMPTY(*n)) { fprintf(stderr, "The heap is empty. \n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } item = heap[1]; temp = heap[(*n)--]; parent = 1; child = 2; while (child <= *n) { if ((child < *n) && (heap[child].key < heap[child + 1].key)) child++; if (temp.key >= heap[child].key) break; heap[parent] = heap[child]; parent = child; child *= 2; } heap[parent] = temp; return item; } void printLI(int n) { printf("Level Order: "); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { printf("%d ", heap[i].key); } putchar('\n'); printf("Inorder: "); iterInorder(heap, n); putchar('\n'); } int main(void) { FILE *fp_read = fopen("input.txt", "r"); int value; element newElement = {0}; int n = 0; while (fscanf(fp_read, "%d", &value) != EOF) { newElement.key = value; push(newElement, &n); } printLI(n); pop(&n); printLI(n); pop(&n); printLI(n); return 0; }
먼저 push가 되는 과정을 보도록 하겠습니다. heap이 full이라는 것의 정의부터 시작해야 합니다. heap이 꽉 차려면 0번부터 시작하는 인덱스의 값이 n - 1이 될 때가 heap이 꽉 찼다고 설정한 때입니다. 이러한 heap이 꽉찬 경우는 저희는 삽입하지 못합니다.
위 그림을 참고하면 될 것 같습니다.
또 이러한 array representation된 배열들은 순회하는 방법이 정해져 있습니다. 먼저 배열을 순서대로 출력하면 Level order가 됩니다. 이를 구현하는 방법은 그냥 배열을 끝까지 (1 ~ n) 순회하면서 돌면 됩니다. 그리고 iterInorder라는 것이 있는데 반복해서 배열에서 중위 순회를 하는 방법을 말합니다. 여기에서는 stack을 사용하는데, 코드를 보시면 이해가 빠르게 되실 겁니다.
'School > DataStructure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Data Structure - Tree ( Selection Tree ) (0) | 2022.05.31 |
|---|---|
| Data Structure - Tree ( BST ) (0) | 2022.05.31 |
| Data Structure - Hashing ( Dynamic Hashing ) (0) | 2022.05.30 |
| Data Structure - Hashing ( Overflow handling ) (0) | 2022.05.30 |
| Data Structure - Hashing ( Hash Functions ) (0) | 2022.05.29 |
